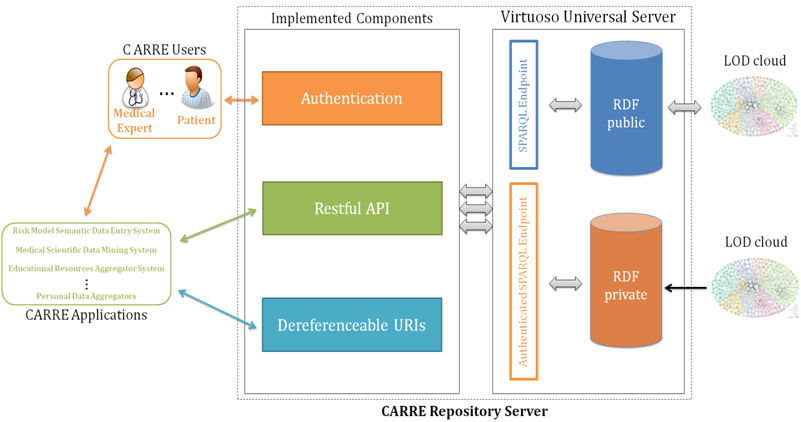
The CARRE repository acts as the central point of information storage for all CARRE applications. It conforms to the principles of the Semantic Web and the guidelines of Linked Data. The Linked Data guidelines can be summarized as follows:
- Use URIs as names for things
- Use HTTP URIs, so that people can look up those names
- When someone looks up a URI, provide useful information, using the standards (RDF, SPARQL)
- Include links to other URIs, so that people can discover more things
Information stored in the CARRE repository consists of “RDF triples”. RDF is a standard format for representing semantic data on the Web; an item of RDF data is a triple, which corresponds to a statement of the form “subject predicate object”. Each term is a URI, often drawn from a standard vocabulary or ontology, making it easy to link triples from different sources – to allow Linked Data. RDF can be accessed through a SPARQL endpoint: SPARQL is a query language, much like SQL in syntax. The triples stored in the CARRE repository are either public or private. For private data, data privacy and security mechanisms have been deployed.
In addition to the above “de facto” standards, we have implemented and published the following web services:
- A CARRE-specific Web API used by CARRE applications that have been prescribed and undergoing development in currently active Work Packages
- Dereferenceable URIs, that allow the seamless access and consumption of CARRE-generated data
- Authentication and authorization services for CARRE users and applications
Authors: George Gkotzis (OU), Allan Third (OU)
Date: 17 Mars 2015